Deep learning (DL)
Deep learning (DL). Machine learning (ML) and more specifically DL are already on the cusp of revolution. They are widely adopted in data centers (Amazon making graphical processing units [GPUs] available for DL, Google running DL on tensor processing units [TPUs], Microsoft using field programmable gate arrays [FPGAs], etc.), and DL is being explored at the edge of the network to reduce the amount of data propagated back to datacenters. Applications such as image, video, and audio recognition are already being deployed for a variety of verticals. DL heavily depends on accelerators and is used for a variety of assistive functions
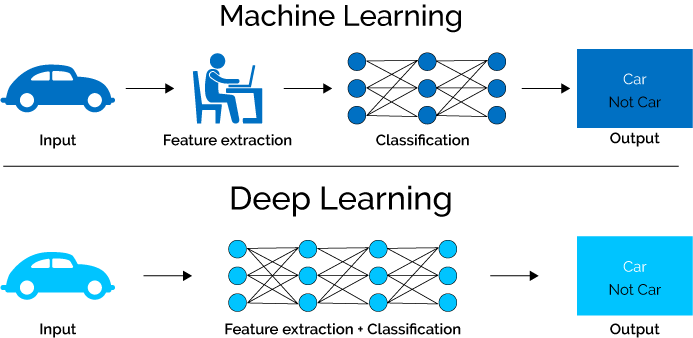
Deep learning (also known as deep structured learning or hierarchical learning) is part of a broader family of machine learning methods based on learning data representations, as opposed to task-specific algorithms
Deep learning is a
machine learning technique that teaches computers to do what comes
naturally to humans: learn by example. Deep learning is a key technology
behind driverless cars, enabling them to recognize a stop sign, or to
distinguish a pedestrian from a lamppost. It is the key to voice control
in consumer devices like phones, tablets, TVs, and hands-free speakers.
Deep learning is getting lots of attention lately and for good reason.
It’s achieving results that were not possible before.
In deep learning, a
computer model learns to perform classification tasks directly from
images, text, or sound. Deep learning models can achieve
state-of-the-art accuracy, sometimes exceeding human-level performance.
Models are trained by using a large set of labeled data and neural
network architectures that contain many layers.
Comments
Post a Comment